Introduction to ZTNA (Zero Trust Network Access)
Protecting our digital information is critical. Traditional network security measures, such as virtual barriers, are no longer as effective as they once were.
Consider a scenario in which you can’t simply trust anyone in your digital space. That is the principle behind Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA). Rather than presuming that everything inside is secure, ZTNA constantly monitors who or what is attempting to access our data, making security more adaptive and robust.
Enterprises often use traditional network security methods like Firewalls, VPN, Network segmentation, IDPS, NAC, EDR, Antivirus etc.
Implementation of ZTNA (Before and After)
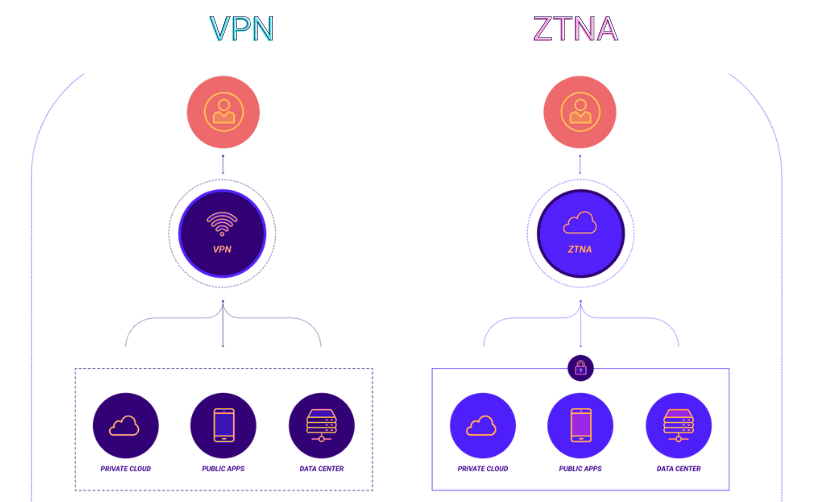
Before ZTNA implementation, traditional security relied on VPNs, which provided broad network access based on location. Users were expected to be trustworthy within the network perimeter, which presented potential risk.
After ZTNA implementation, security became more user-centric. Access is now detailed, based on user identification and context, eliminating dependency on a static perimeter while offering flexible, secure connectivity to users working from anywhere.
| Aspects | Before ZTNA | After ZTNA |
| Security approach | Trusted entities assumed | Continuous verification for enhanced security |
| Adaptability | Less adaptability to change | Adapts to Modern work practices, supporting |
| Complexity | Simple to manage | May be more complex during the implementation |
| Access control | Broad access granted. | Least-privilege access reduces potential risks. |
| Visibility | Limited visibility into activities. | Enhanced visibility for better threat detection. |
| Prevention focus | Emphasis on preventing threats at the edge. | Shifts from prevention-only to detection and response. |
| Remote access | Traditional VPNs for remote access. | Secure and user-friendly remote access. |
| Learning curve | Familiar practices. | May involve a learning curve for new access methods. |
| Resource requirement | Typically less demanding. | May require additional resources for implementation. |
| Implementation | Familiarity with traditional models. | The Transition may pose challenges. |
Why do Organizations need ZTNA (Zero Trust Network Access)?
Incidents such as the Colonial Pipeline ransomware assault, have underlined the need for a stronger security posture. The attack, carried out by a criminal group known as DarkSide, caused the shutdown of the United States major fuel pipeline. The attackers accessed the pipeline’s network using a hacked VPN account.
ZTNA can assist avoid such attacks by,
Increasing use of cloud services: As businesses rely more on cloud services for data storage and processing, the danger of unwanted access or data breaches rises. ZTNA’s zero trust ensures that only trusted users and devices have access to critical data, lowering the danger of illegal access.
Remote work and mobile devices: As remote work and mobile device use have grown in popularity, so has the number of people and devices connecting to the organization’s network. ZTNA’s ability to regulate access based on user identity and device trustworthiness helps to secure the organization’s network from potential attacks.
Cybersecurity threats: The growing amount of cybersecurity threats, including ransomware, phishing assaults, and distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks, emphasizes the importance of a strong security posture. ZTNA’s multi-factor authentication, least privilege access, and continuous monitoring and control serve to safeguard the organization’s network from potential attacks.
Regulatory compliance: Organizations may be required to follow a variety of regulations and standards, including the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act. Organizations can achieve these compliance standards by leveraging ZTNA’s enhanced security posture and threat protection.
Improved security posture: ZTNA’s comprehensive network security approach creates a more secure and reliable environment for the organization’s users, devices and applications. This can help strengthen the organization’s overall security posture and lower the likelihood of a security breach.
ZTNA Architecture and Infrastructure Requirements
It varies depending on the organization’s specific needs and requirements. Here are some factors that can influence the size of ZTNA:
Number of users and devices: ZTNA solutions vary in handling users and devices based on vendors, deployment, and hardware. They can adapt to support thousands of users and may require extra infrastructure for larger deployments. Organizations should evaluate scalability based on user size, growth, and conduct testing for best performance.
Geographic distribution: The geographic distribution of users and devices may have an impact on ZTNA’s size. For example, if users and devices are spread out over several locations, the ZTNA Framework may require expansion to handle increasing network traffic and potential threats.
Types of devices: The type of devices in an organization can influence the size of ZTNA. For example, if a company has a significant number of IoT devices, the ZTNA setup to manage more network traffic and potential threats. Considering device type and other factor helps create a strong, adaptive ZTNA Solution to improve organisational security.
Security requirement: An organization’s security requirements can have an impact on ZTNA size. For example, if a firm has stringent regulatory compliance requirements may demand strengthening the ZTNA structure by including advanced security measures.
Budget and resources: The money and resources available to an organization can influence the size of ZTNA. For example, if a company has a limited budget and resources, its ZTNA infrastructure may need to be more cost-effective to meet its security requirements.
Organizations should carefully consider these factors when determining the appropriate size of their ZTNA infrastructure.
Why Vays?
Vays Infotech is one of the top partners of Fortinet, Forcepoint and other industry leaders. We provide services to our clients in the following ways
ZTNA service provider: Specialize in offering ZTNA as a service to provide cloud-based solutions that organizations can subscribe to, eliminating the need for extensive infrastructure investments.
Implementation and Integration: Assist organizations in implementing ZTNA solutions. This involves integrating ZTNA into the existing network architecture, defining access policies, and ensuring a smooth transition to the new security model.
Security Consultation: Offer services to help organizations assess their security needs and tailor ZTNA solutions to their specific requirements.
Managed Security Services: Managed security service providers (MSSPs) may offer ongoing monitoring, maintenance, and support for ZTNA implementations. This ensures that the security measures remain effective and up-to-date.
Training and Support: They will provide training for IT staff and end-users to ensure that they understand how to use and benefit from the ZTNA solution. They also provide ongoing support for any issues that may arise.
Customization and Integration: They tailor ZTNA solutions to the unique needs of each organization. This involves customizing access policies, integrating with existing security infrastructure, and ensuring compatibility with other IT systems.
To know more on our IT Services, click here on Network Security

